Rainfall
Daily rainfall data from all local rainfall stations (Met Éireann) are used to calculate average annual rainfall within catchment.
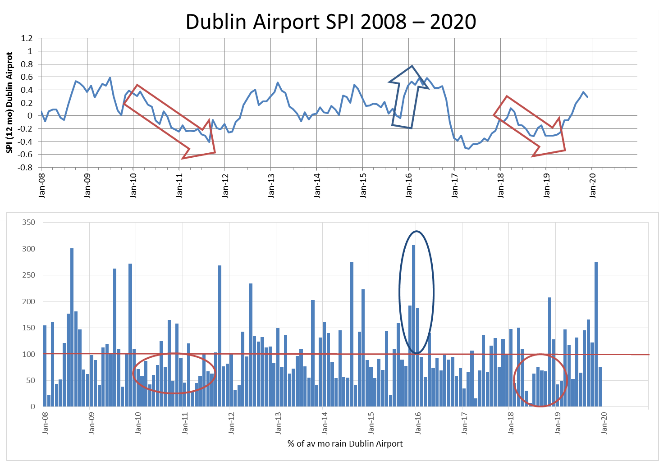
Standardised Precipitation Index (SPI) (SPI; McKee 1993) is the number of standard deviations that observed cumulative precipitation deviates from the climatological average.
Daily Potential Evapotranspiration (PE) data is calculated from synoptic station(s) data within catchment.
Rainfall and PE calculated from the recharge map data are used d to calculate effective rainfall and an initial estimate of the range of outflow from the catchment which is compared to hydrometric data.
Surface water
We are using data from the OPW, the EPA, Local Authorities (LA) and ESB currently monitor surface level and/or flow (hydrometric data) at different locations within the catchments.
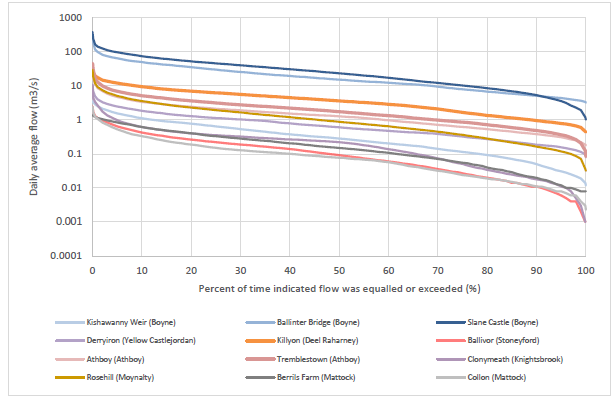
Flow statistics from this hydrometric data are compared to the calculated Q95s from EPA hydrometric data. The flow duration curves are used for characterising runoff at the corresponding gage.
If there are no hydrometric stations in the catchment modelled estimates of flow (Naturalised and Influenced Mean Flows and Q95s) from EPA's QUBE model is used.
Flow duration curves for rivers within the Boyne
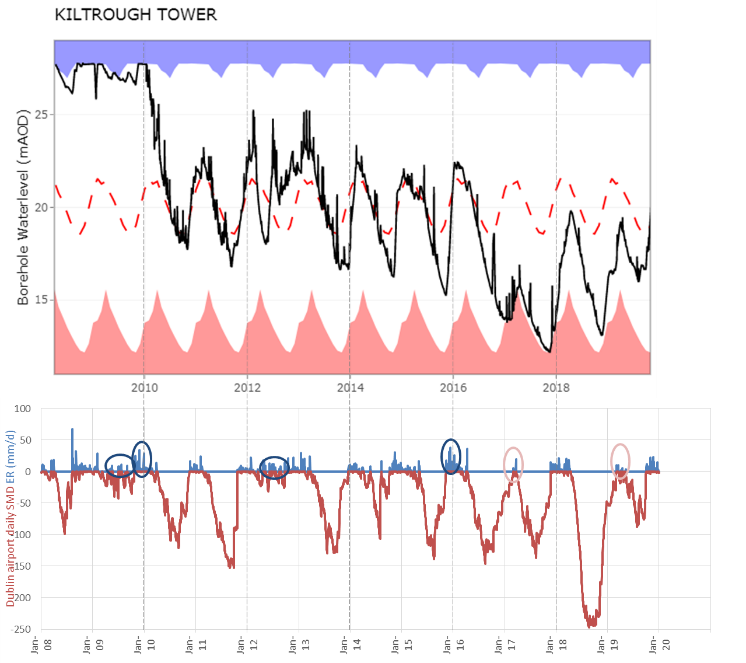
Groundwater level
Groundwater hydrographs provide direct evidence of how aquifers are behaving.
We are using groundwater hydrographs from the EPA's national monitoring network to better understand the impacts of recharge, abstraction and climate change within each catchment.
To interpret the hydrographs, we are using calculated standardised precipitation indices and effective rainfall.