 Credit: 2009, Geoschol Project, Adam Stuart Smith and Patrick Wyse Jackson
Credit: 2009, Geoschol Project, Adam Stuart Smith and Patrick Wyse Jackson
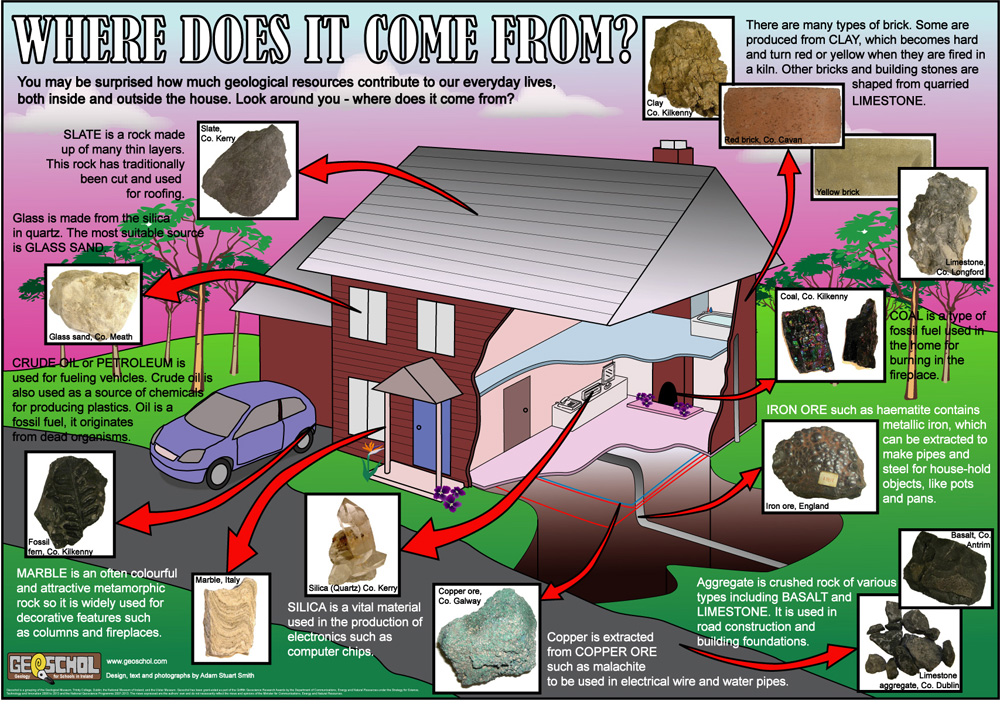
Foundations: the foundations are usually constructed from concrete. Concrete is a mixture of fine aggregates such as sand, coarse aggregates made from crushed rock, cement, made from crushed limestone, and water.
The sand for concrete can be quarried from sand pits formed from glacial materials here in Ireland or it may be dredged from the sea.The coarse aggregates are quarried locally and crushed to an appropriate size.
The cement is formed by crushing limestone to a fine powder and heating it along with shale to a high temperature. It is ground down again and a small amount of gypsum is added. Water is added to this mixture and it can then be poured to form solid foundations for the structure to be built on.
Walls: most modern homes are built with concrete blocks, these are made using the same process as described for the construction of foundations. Some homes have walls constructed of bricks which are made from clay, this clay contains minerals such as shale. Older buildings are often built using cut stone, the most popular rocks for this purpose are limestone, granite and sandstone.
- Limestone is a popular building material used in structures such as the GPO and the Four Courts in Dublin. It is easily cut and carved making it a popular choice for construction. Limestone is found in every county of Ireland except for Antrim, it is quarried throughout the country and has widespread uses in the construction industry.
- Granite is an igneous rock and is incredibly hard wearing however this can make it difficult to work with. It is often used for more decorative features such as lintels and window sills. Granite is quarried in places such as Galway, Wicklow and the Mourne Mountains.
- Sandstone like limestone is a sedimentary rock and is easy to cut and carve. Sandstone is quarried in various location across the country.
- As mentioned above concrete blocks are now the most common material for the construction of walls however, stone cladding has now become a popular practice. The wall is constructed using concrete blocks but thin layers of cut rock are used to cover the surface.
- Inside the house non load-bearing walls are constructed from plasterboard. This plasterboard along with the plaster used to skim the walls is made from a mineral called Gypsum which is quarried in Kingscourt in Co. Cavan.
Windows and doors: the frames for windows and doors can be made from a variety of geological materials such as aluminium, steel and PVC. Aluminium and the raw materials of steel, iron and carbon, can be mined from the Earth and PVC is a product of petrochemical industry as it is derived from crude oil.
The glass for our windows and doors is made by melting together several minerals at very high temperatures. Silica sand is the main ingredient, it is combined with limestone and sodium carbonate and heated to temperatures of up to 17000C in a furnace. Although these ingredients are all available in Ireland most of the glass we use is imported into the country.
Roof: slate is a metamorphic that was traditionally used in roofing. Local slate quarries include those in Clare, Tipperary, Cork and Kerry however the majority of slate was imported from North Wales. Although still used in restoration work Slate is no longer a commonly used as a roofing material. It has been replaced by materials such as clay tiles, artificial slate and mineral felt.
Plumbing: copper is the main material used in pipework for central heating systems. Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, is also commonly used as a material for plumbing fittings. Both of these minerals have been mined in Ireland.
Gutters and drains are now made from PVC however older homes may have cast iron pipes and gutters.
Electrics: copper and PVC are the main materials used in the production of electric wiring used in the home. Old light bulbs used to use tungsten in their filament however these bulbs are no longer used due to energy inefficiency.
Interiors: many fittings within the home are made from metals such as aluminium, brass and steel. Plastics are widely used in the home and these are derived from oil. Ceramics commonly used in wall and floor tiles and bathroom fittings are made from clay and minerals such as feldspar and flint. Rock can be used decoratively in the home for example hard wearing granite used in kitchen worktops and marble, a metamorphic rock, used to made fireplaces.
Driveway: can be made from poured concrete, concrete slabs, gravel or asphalt. Asphalt commonly referred to as tarmac is a made by mixing fine grain aggregate with bitumen. Bitumen is a naturally occurring component which is now commonly synthesised from oil.